
Winter arrives on December 21. The shortest day of the year. There is never a shortage of things to do in the garden, even in winter. Update your garden records from last season and review your garden design. What worked and what can be improved this coming growing season? Now is the time to plan layout changes for the garden and begin mapping crop rotations and successions for the coming year.
Spring seed catalogs will arrive soon so this is a good time to prepare seed and plant orders for spring. Give some thought to how much to plant this year; plan a continuous harvest.
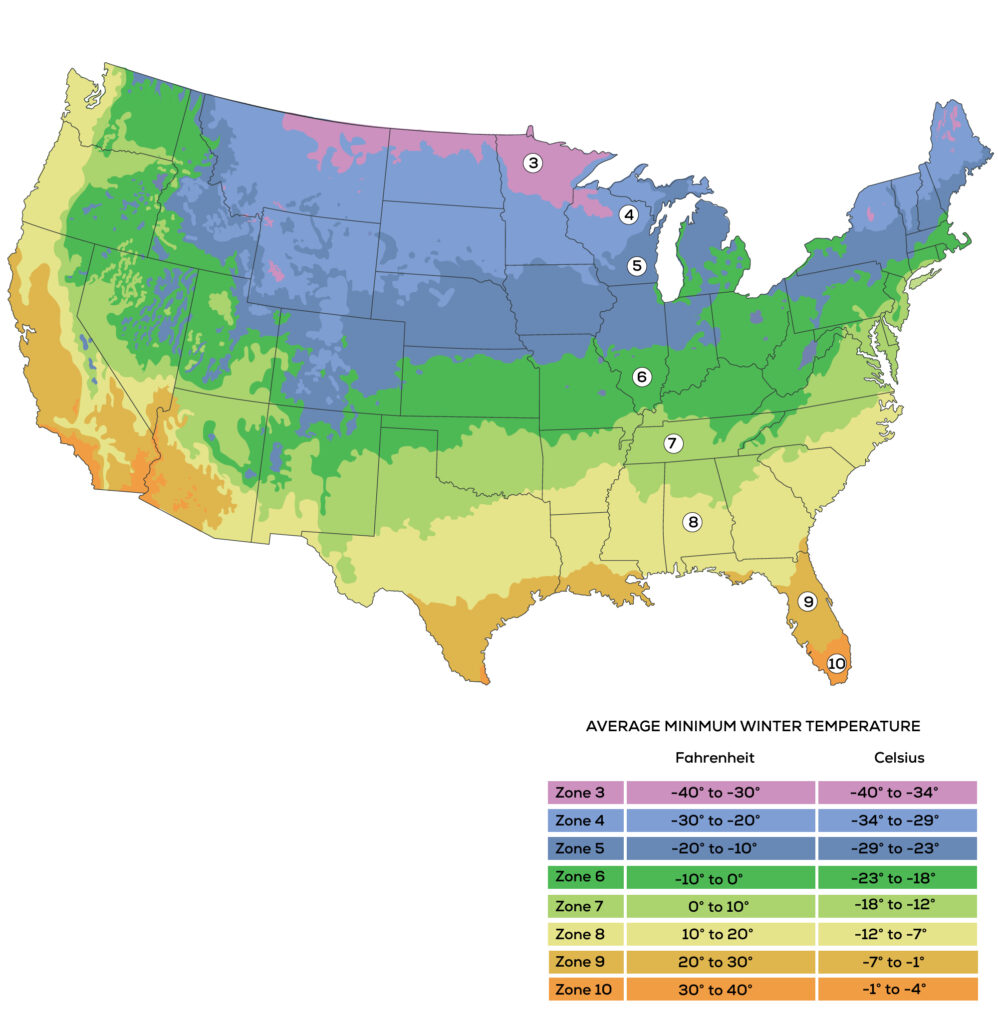
Here follows this month’s roundup of vegetable garden opportunities and tasks. Use the map to determine in which USDA zone you are located.
Zones 9b-11:
Perennials such as asparagus, artichokes, horseradish, and rhubarb can be planted. Make new strawberry beds. Plant cool-weather crops in the garden or cold frame. Sow the seeds of artichokes, asparagus, beets, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, celery, cress, endive, kale, kohlrabi, head lettuce, leaf lettuce, leeks, mustard, parsley, parsnip, English peas, potatoes, onions, radish, salsify, winter spinach, Swiss chard, turnips. Sow quick-maturing crops such as lettuce, radishes, and spinach where you will plant tomatoes, melons, and corn in spring. Divide and reset herbs. Divide chives.
Harvest crops from the garden and cold frame. Harvest late summer planted kohlrabi, carrots, beets, and turnips while young and tender. Harvest broccoli and Brussels sprouts; remove bottom sprouts and leaves first and work your way up. Pick peas to keep them coming. Start harvesting the outside stalks of celery. Harvest outside leaves of lettuce first, return for other leaves as they mature; this is known as cut-and-come-again harvesting.
Fertilize, thin, and water crops sown in early autumn. Fertilize broccoli and Brussels sprouts with a side-dressing of aged compost.
Use row covers when necessary to hold heat around crops; fluff straw over plants when there is a chill. If the temperature is forecast to go below 28°F (-2.2°C) protect broccoli heads, cauliflower heads, lettuce, and flowers of English peas, snow peas, and edible-podded peas. Tie leaves over cauliflower heads when cold temperatures are forecast.
Watch the weather and avoid setting out transplants when a freeze is predicted. Crops that will tolerate temperatures down to the low 20sF with little or no damage are Swiss chard, Chinese cabbage, kohlrabi, mustard greens, radish (will resprout from roots), turnips (will resprout from roots), and spinach. Crops that will survive temperatures in the low 20sF and teens are beets, Brussels sprouts, carrots, celery, collards, garlic, kale, onions, leeks, and shallots.
Clean crop debris from empty parts of the garden. Dig organic matter—aged manure and aged compost– into the soil or plant a cover crop where you are not planting this winter.
Ventilate the cold frame or lift the flaps on plastic tunnels on days warmer than 42°F (5.6°C).
Prepare seed orders for spring planting.

Zone 8
Plant cool-weather crops in the garden, plastic tunnel, or cold frame. Sow in the plastic tunnel or cold frame broccoli, cabbage, carrots, cabbage, cauliflower, cauliflower, endive, kale, kohlrabi, head and leaf lettuce, mustard, Bermuda onion seed, English peas, radish, spinach, and turnips. Plant asparagus crowns in heavily manured soil. Plant Rhubarb now. Plant perennial herbs such as horseradish, mint, rosemary, and sage. Strawberries can be planted in some regions.
Harvest late summer and autumn-planted crops from garden, plastic tunnel, and cold frame. Ventilate the plastic tunnel and cold frame on warm days.
Side-dress crops with aged compost. Dig organic matter or spread aged manure across the spring garden site or plant cover crops in parts of the garden where you will not be planting this winter.
Zone 7
Cool-season winter vegetables can still be planted in cold frames that maintain a temperature of greater than 50ºF (10 ºC); growth will be slow. See suggestions for crops you can grow in a plastic tunnel or cold frame this winter above in Zone 8. You will not plant in the open garden again until late winter, February. Begin planning next spring’s garden. Plan crop locations, rotations, and successive plantings for next year.
Harvest late crops still in the garden or from the plastic tunnel or cold frame. Lift root crops stored in the garden under mulch as needed—parsnips, beets, carrots, turnips.
Ventilate the cold frame or plastic tunnel on warm days. Check windbreaks, mulches, and winter protection; be prepared for winter storms. Spread straw, chopped leaves, or other mulch across the garden when the ground is frozen. Prepare seed and plant orders for spring.

Zone 6
See suggestions for crops you can grow in a plastic tunnel or cold frame this winter above in Zone 8. You will not plant in the open garden again until early spring, March. Start herbs indoors or take cuttings and root them in a sterile growing medium. Plant microgreens indoors; grow them under grow lights or in a sunny window. Sprout seeds to add to salads.
Lift root crops stored in the garden under mulch as needed. Harvest late crops from the plastic tunnel or cold frame; ventilate the tunnel or frame on warm days.
Check windbreaks, mulches, and winter protection before winter storms arrive. Mulch the garden when the ground is frozen. Prepare seed and plant orders for spring.

Zones 4-5
Sow cool-season crops in the cold frame. See suggestions for crops you can grow in a plastic tunnel or cold frame this winter above in Zone 8. You will not plant in the open garden again until mid-spring, April, later in Zones 1-3.
Start herbs indoors or take cuttings and root them in a sterile growing medium. Plant microgreens indoors; grow them under grow lights or in a sunny window. Sprout seeds to add to salads.
Check all stored vegetables to make sure no decay has set in. Keep stored apples at 35° to 40°F (1.7-4.4°C).
Harvest late crops from the plastic tunnel or cold frame; ventilate the tunnel or frame on warm days. Vegetables in tunnels or frames benefit from air circulation on warm days. Lift root crops stored in the garden under mulch as needed.
Work compost and green manure into beds. Turn under last year’s beds. Add lime to the soil if it is acid. Mulch the garden when the ground is frozen. Check windbreaks, mulches, and winter protection.
Make planting plans for next spring; this will get you ready to order seeds and plants for spring next month.
Fruit
Zones 9-11: Plant fruit trees, berries, and grapes. Stake newly planted fruit trees. Prune fruit trees and bushes while dormant. Apply dormant oil sprays after fruit trees have dropped all of their leaves.
Zones 7-8: Plant bare-root fruit stock if the soil is still workable. Plant strawberry, boysenberry, and youngberry plant in the garden now. Prune established fruit trees, bushes, and grapevines when leaves are gone. Clean up dropped fruit and leaves
Zones 1-6: Install mouse guards and other winter protection. Check fruit trees for overwintering pests; destroy pests. Plan spring plant orders.















